Air pollution is one of the most pressing problems of our century. Large industrial facilities such as power plants, cement factories, steel mills, and chemical plants produce enormous quantities of gases and airborne particles, the release of which, if left untreated, can have devastating consequences for human health and the environment. Electrostatic precipitators (ESPs) or electrostatic scrubbers are among the most commonly used devices for removing solid particles and liquid droplets from exhaust gases.
What is an electric floor cleaning machine?
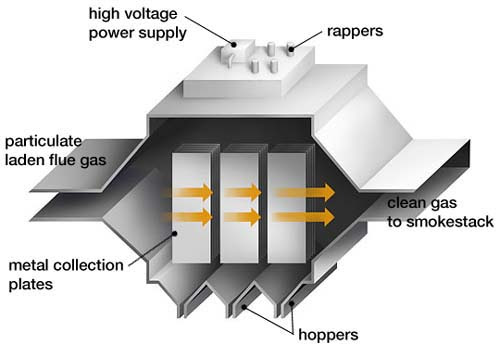
An electrostatic precipitator is a device that uses a strong electric field to charge particles suspended in a gas and then attracts them to a collecting plate. This method can separate even the smallest particles in the micrometer to submicrometer range.

How does extrasensory perception work?
The operation of an ESP is usually divided into four main phases:
-
Contaminated gas inlet: Gas containing suspended particles enters the EF chamber.
-
Particle ionization: The discharge electrode generates a high voltage and ionizes the surrounding gas, giving the suspended particles an electrical charge.
-
Particle collection: Charged particles move to oppositely charged collector plates and are deposited.
-
Discharge and cleaning: Particles collected on the plates are regularly removed using a shaking system or mechanical vibration and collected in special tanks.
Types of electrostatic precipitators
ESPs are generally divided into two categories:
-
Dry electrostatic precipitator:
-
The most commonly used ESP type
-
Removes dry particles such as dust, soot and ash.
-
It is widely used in thermal power plants and the cement industry.
-
-
Wet electrostatic precipitator:
-
Suitable for wet and viscous particles or liquid aerosols.
-
Wash the drip plate with water or liquid spray.
-
Widely used in the chemical and oil refining industries.
-
Advantages of ESP
-
High efficiency: Can remove more than 99% of suspended particles .
-
Suitable for fine particles: effective for particles up to 0.01 µm in diameter.
-
Reduce air pollution: Promote compliance with environmental standards
-
Pressure drop: In contrast to mechanical filters, there is a negligible pressure drop.
-
Long lifespan: With proper care, it can be used for decades.
Disadvantages of ESP
-
High acquisition costs (installation and purchase of equipment)
-
More space is required to install the devices .
-
Particles with low conductivity are less effective.
-
Sensitivity to changes in gas composition (humidity, temperature, chemical composition)
ESP application
Electrostatic precipitators are used in many industries, including:
-
Thermal power plants (fly ash and smoke removal)
-
Cement and gypsum industry
-
Steel and foundry industry
-
Chemical and petrochemical industry
-
oil refinery
-
Paper mills and wood processing plants
-
Pharmaceutical industry (removal of dust particles and some fumes)
Important points for the operation and maintenance of ESP
-
To maintain optimal performance, voltage and current must be continuously monitored.
-
The panels should be cleaned regularly to prevent the accumulation of particles that can affect performance.
-
Insulation is important to prevent electrical leakage .
-
To avoid corrosion or breakage, regular inspection of the electrodes and plates is necessary.
The future of extrasensory perception
Due to increasingly stringent environmental regulations, the use of electrostatic discharge (ESD) filters is increasing. The new generation of ESD filters offers the following features:
-
Intelligent management of digital efficiency
-
Reduce energy consumption
-
More resistant to corrosion and heat.
-
More compact and efficient design
They ensure greater efficiency and lower operating costs.

Electrostatic precipitators ( ESPs ) are among the most effective technologies for removing particulate matter from industrial gases. Their high efficiency , ability to remove fine dust, and long service life make them ideal for large-scale industrial applications. Despite their high initial cost, they can reduce environmental pollution, improve safety, and ensure long-term compliance with environmental regulations.